10 Best Blacksmith Forges 2025 in the United States
Winner
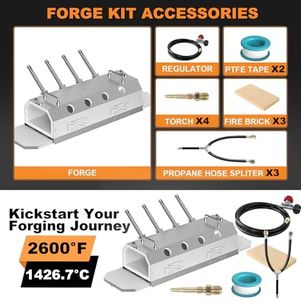
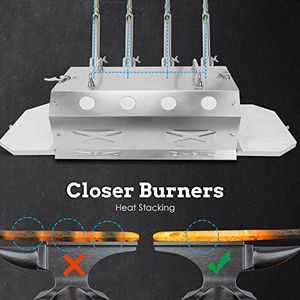
Nelyrho Gas Propane Forge 2600°F,Double Door,Large Capacity,Portable Equipment,Knife Making(Stainless Steel) Blacksmithing Farrier tool,Gas Welding Kits, Forge Kit (Four Burners)
The Nelyrho Gas Propane Forge is a large-capacity equipment designed for blacksmithing, particularly suitable for knife making and farrier work. Its four burners ensure even heat distribution, making it ideal for heating long rods. The beveled nozzle design enhances the interaction between flame and metal, speeding up the heating process and ensuring uniform temperature.
Most important from
90 reviews
VEVOR Portable 2 Burner Propane Forge, 2600°F Metal and Knife Blacksmithing Forges, Large Capacity Farrier Forging Tools and Equipment, Complete Mini Forge Kit
The VEVOR Portable 2 Burner Propane Forge is a solid option for blacksmithing, especially for those working with various metals. One of its standout features is its ability to reach temperatures up to 2600℉, making it capable of handling a wide range of forging tasks. The forge heats up quickly, within three minutes, and offers the flexibility of using one or both burners, which can help save on propane costs.
Most important from
201 reviews
Nelyrho Portable Blacksmith Beginner Forge Kit With 30PSI Regulator, Single Burner Professional Artists Hobby Knife Making Blacksmith Tools
The Nelyrho Portable Blacksmith Beginner Forge Kit is designed with beginners in mind, providing a convenient and efficient entry point into blacksmithing. Its compact size, with external dimensions of 9.5 x 8.7 x 5.5 inches, and internal dimensions slightly smaller, makes it a highly portable option, ideal for those who may not have a dedicated workshop space. Made from stainless steel, it promises durability and longevity. The forge is equipped with a single burner and includes a 30PSI regulator, allowing users to quickly reach and maintain high temperatures up to 2600℉, which is sufficient for most basic blacksmithing needs. This means you can start shaping metals, such as for knife making, relatively quickly and without needing additional materials like hardeners or refractory components.
Most important from
90 reviews
Top 10 Best Blacksmith Forges 2025 in the United States
Winner
9.9 score
Nelyrho Gas Propane Forge 2600°F,Double Door,Large Capacity,Portable Equipment,Knife Making(Stainless Steel) Blacksmithing Farrier tool,Gas Welding Kits, Forge Kit (Four Burners)
Nelyrho Gas Propane Forge 2600°F,Double Door,Large Capacity,Portable Equipment,Knife Making(Stainless Steel) Blacksmithing Farrier tool,Gas Welding Kits, Forge Kit (Four Burners)
Chosen by 1448 this week
VEVOR Portable 2 Burner Propane Forge, 2600°F Metal and Knife Blacksmithing Forges, Large Capacity Farrier Forging Tools and Equipment, Complete Mini Forge Kit
VEVOR Portable 2 Burner Propane Forge, 2600°F Metal and Knife Blacksmithing Forges, Large Capacity Farrier Forging Tools and Equipment, Complete Mini Forge Kit
Nelyrho Portable Blacksmith Beginner Forge Kit With 30PSI Regulator, Single Burner Professional Artists Hobby Knife Making Blacksmith Tools
Nelyrho Portable Blacksmith Beginner Forge Kit With 30PSI Regulator, Single Burner Professional Artists Hobby Knife Making Blacksmith Tools
Nelyrho Portable Blacksmith Beginner Forge Kit with 30PSI Regulator, Dual Burners Professional Artists Hobby Knife Making Blacksmith Tools (Double Burners)
Nelyrho Portable Blacksmith Beginner Forge Kit with 30PSI Regulator, Dual Burners Professional Artists Hobby Knife Making Blacksmith Tools (Double Burners)
ATkrou Gas Propane Forge 2600°F,Double Doors,Large Capacity,Portable Equipment,Knife Making(Stainless Steel) Blacksmithing Farrier tool,Gas Welding Kits, Forge Kit GY200
ATkrou Gas Propane Forge 2600°F,Double Doors,Large Capacity,Portable Equipment,Knife Making(Stainless Steel) Blacksmithing Farrier tool,Gas Welding Kits, Forge Kit GY200
Nelyrho Propane Blacksmith Beginner Forge Kit with 30PSI Regulator, Three Burners Artists Hobby Knife Making Blacksmith Tools (Three Burners)
Nelyrho Propane Blacksmith Beginner Forge Kit with 30PSI Regulator, Three Burners Artists Hobby Knife Making Blacksmith Tools (Three Burners)
8.2 score
Cast Master Elite CMF 3000 Blacksmith Forge - Triple Burner Propane Blacksmithing Forge Burner - Large Capacity Beginner to Advanced Blacksmith Furnace and Forge Tools Starter Kit
Cast Master Elite CMF 3000 Blacksmith Forge - Triple Burner Propane Blacksmithing Forge Burner - Large Capacity Beginner to Advanced Blacksmith Furnace and Forge Tools Starter Kit
Our technology thoroughly searches through the online shopping world, reviewing hundreds of sites. We then process and analyze this information, updating in real-time to bring you the latest top-rated products. This way, you always get the best and most current options available.